Bit Serial Transmission
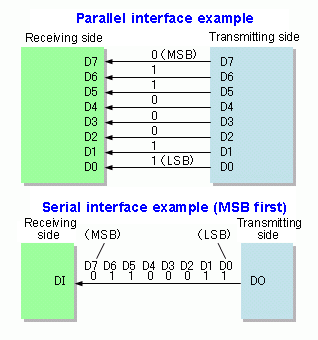
Most data communications over networks occurs via serial-data transmission. Data bits transmit one at a time over some communications channel, such as an or a wireless path. Typifies the digital-bit pattern from a computer or some other digital circuit.
Asynchronous serial communication is a form of serial communication in. A common kind of start-stop transmission is. Mechanical teleprinters using 5-bit. Data transmission refers to the movement of data in form of bits between two or more digital devices.Types of Data Transmission. Known as bit-serial transmission.
This data signal is often called the baseband signal. The data switches between two voltage levels, such as +3 V for a binary 1 and +0.2 V for a binary 0. Other binary levels are also used. 1, again), the signal never goes to zero as like that of return-to-zero (RZ) formatted signals.

Non-return to zero (NRZ) is the most common binary data format. Data rate is indicated in bits per second (bits/s). Bit Rate The speed of the data is expressed in bits per second (bits/s or bps).
The data rate R is a function of the duration of the bit or bit time (T B) (Fig. 1, again): Related: R = 1/T B Rate is also called channel capacity C. If the bit time is 10 ns, the data rate equals: R = 1/10 x 10 –9 = 100 million bits/s This is usually expressed as 100 Mbits/s. Overhead Bit rate is typically seen in terms of the actual data rate. Yet for most serial transmissions, the data represents part of a more complex protocol frame or packet format, which includes bits representing source address, destination address, error detection and correction codes, and other information or control bits. In the protocol frame, the data is called the “payload.” Non-data bits are known as the “overhead.” At times, the overhead may be substantial—up to 20% to 50% depending on the total payload bits sent over the channel.
Sponsored Resources: • • For example, an Ethernet frame can have as many as 1542 bytes or octets, depending on the data payload. Payload can range from 42 to 1500 octets. With a maximum payload, the overhead is only 42/1542 = 0.027, or about 2.7%. It would be even greater if the payload was anything smaller. This relationship is usually expressed as a percentage of the payload size to the maximum frame size, otherwise known as the protocol efficiency: Protocol efficiency = payload/frame size = 1500/1542 = 0.9727 or 97.3% Typically, the actual line rate is stepped up by a factor influenced by the overhead to achieve an actual target net data rate.
In One Gigabit Ethernet, the actual line rate is 1.25 Gbits/s to achieve a net payload throughput of 1 Gbit/s. In a 10-Gbit/s Ethernet system, gross data rate equals 10.3125 Gbits/s to achieve a true data rate of 10 Gbits/s.
Cellmax Ret Software Engineering. The net data rate also is referred to as the throughput, or payload rate, of effective data rate. Baud Rate The term “baud” originates from the French engineer Emile Baudot, who invented the 5-bit teletype code. Baud rate refers to the number of signal or symbol changes that occur per second. A symbol is one of several voltage, frequency, or phase changes. NRZ binary has two symbols, one for each bit 0 or 1, that represent voltage levels. In this case, the baud or symbol rate is the same as the bit rate.
However, it’s possible to have more than two symbols per transmission interval, whereby each symbol represents multiple bits. With more than two symbols, data is transmitted using modulation techniques. When the transmission medium can’t handle the baseband data, modulation enters the picture.